What is the difference between Celadrin and glucosamine?
Celadrin and glucosamine contribute to joint health in different ways. Celadrin has fatty acids that help with flexibility of cell membranes and therefore joints and muscles, while glucosamine helps by supporting healthy cartilage and synovial fluid.
What is Celadrin made from?
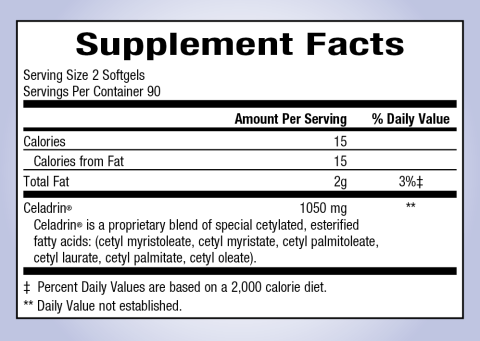
Celadrin is made from a patented complex blend of specially prepared fatty acids derived from beef.
How much should I take?
2 softgels taken once per day with or without a meal, or as directed by a health professional.
Is Celadrin effective?
Yes! In a study with 64 participants with occasional knee discomfort, adults who were given the ingredients in Celadrin experienced statistically significant improvement in joint function as compared to the placebo group.1
What are the side effects?
No side effects have been reported for oral consumption of the fatty acids found in Celadrin.
Is Celadrin safe?
Celadrin is safe when taken in appropriate amounts as described on the product label. Oral Celadrin has been taken up to 68 days in research studies without adverse effects.1
Is Celadrin a blood thinner?
There is no current evidence that Celadrin thins the blood. However, individuals taking warfarin (Coumadin) should consult with their health professional prior to taking this dietary supplement.
Can I take Celadrin with other supplements?
It may be used along with other natural joint health supplements such as Glucosamine Sulfate (GLS), Chondroitin Sulfate (CS), or MSM, empowering them to perform faster and more efficiently in building joint cartilage. Celadrin has complementary function to the omega-3 fatty acids and can be taken together with them, as found in fish oil or flaxseed oil.
Can I use Celadrin cream and take softgels at the same time?
Celadrin and glucosamine contribute to joint health in different ways. Celadrin has fatty acids that help with flexibility of cell membranes and therefore joints and muscles, while glucosamine helps by supporting healthy cartilage and synovial fluid. Oral and topical Celadrin have been found to be equally effective. It is best to start with one or the other. Talk with your health professional before using both together.